UPSC Indian Modern History 7 (Old Year Questions)
You'll Read
UPSC Indian Modern History 7 (Old Year Questions)
Quiz-summary
0 of 20 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
Information
20 questions based on Indian Modern History.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 20 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 20
1. Question
1 pointsWhere was the First Session of the Indian National Congress held in December 1885?
Correct
Ans b
The first Session of INC was held from 28-31 December 1885, and was attended by 72 delegates. The first meeting was scheduled to be held in Pune, but due to a plague outbreak there, the meeting was later shifted to Bombay.Incorrect
Ans b
The first Session of INC was held from 28-31 December 1885, and was attended by 72 delegates. The first meeting was scheduled to be held in Pune, but due to a plague outbreak there, the meeting was later shifted to Bombay. -
Question 2 of 20
2. Question
1 pointsMatch List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
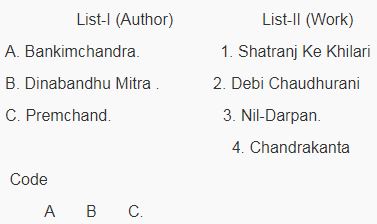 Correct
Correct
Ans c
Bankim Chandra was a Bengali poet, novelist, essaying and journalist, most famous as the author of Vande Mataram or Bande Mataram, that inspired the freedom fighters of India, and was later declared the National Song of India. His novel Chaudhurani, was published in 1884. Dinabandhu Mitra the Bengali dramatist, was born in 1830 at Chouberia in Nadia, and was the son of Kalachand Mitra. His given name was Gandharva Narayan, but he changed it to Dinabandhu Mitra. Mitra stormed the social and the literacy cirle of Bengal by his most notably play Nildarpan in the year 1860. It was published from Dhaka and soon after its publication it ignited a major argument in the newspapers. Munshi Premchand, was one of the greatest literacy figures of modern Hindi and Urdu literature. Shatranj ke khiladi is a story in Hindi written by him. Premchand’s Urdu version is titled Shatranj ki bazi. The story depicts decadent royalty of Central North India. It is set around the life of Nawabs of Lucknow, local feudal lords, in the eighteenth century.Incorrect
Ans c
Bankim Chandra was a Bengali poet, novelist, essaying and journalist, most famous as the author of Vande Mataram or Bande Mataram, that inspired the freedom fighters of India, and was later declared the National Song of India. His novel Chaudhurani, was published in 1884. Dinabandhu Mitra the Bengali dramatist, was born in 1830 at Chouberia in Nadia, and was the son of Kalachand Mitra. His given name was Gandharva Narayan, but he changed it to Dinabandhu Mitra. Mitra stormed the social and the literacy cirle of Bengal by his most notably play Nildarpan in the year 1860. It was published from Dhaka and soon after its publication it ignited a major argument in the newspapers. Munshi Premchand, was one of the greatest literacy figures of modern Hindi and Urdu literature. Shatranj ke khiladi is a story in Hindi written by him. Premchand’s Urdu version is titled Shatranj ki bazi. The story depicts decadent royalty of Central North India. It is set around the life of Nawabs of Lucknow, local feudal lords, in the eighteenth century. -
Question 3 of 20
3. Question
1 pointsWho among the following gave systematic critique of the moderate politics of the Indian National Congress in a series of articles entitled New Lamps for Old?
Correct
Ans a
In 1893, Shri Aurobindo started writing political articles under the general title ‘New Lamps For Old’, at the instance of his Cambridge friend, K. G. Deshpandey, who edited the English section of an Anglo-Marathi paper known as the ‘Indu Prakash’. These articles constituted a direct, invasive and eloquent attack on the Indian National Congress, whose policies Shir Aurobindo regarded as a process of futile petition and protest. Shri Aurobindo gave a stirring call to his countrymen to organize all the forces in the nation for revolutionary action as the sole effective policy for the attainment of our independence.Incorrect
Ans a
In 1893, Shri Aurobindo started writing political articles under the general title ‘New Lamps For Old’, at the instance of his Cambridge friend, K. G. Deshpandey, who edited the English section of an Anglo-Marathi paper known as the ‘Indu Prakash’. These articles constituted a direct, invasive and eloquent attack on the Indian National Congress, whose policies Shir Aurobindo regarded as a process of futile petition and protest. Shri Aurobindo gave a stirring call to his countrymen to organize all the forces in the nation for revolutionary action as the sole effective policy for the attainment of our independence. -
Question 4 of 20
4. Question
1 pointsWhich one of the following was a journal brought out by Abul Kalam Azad?
Correct
Ans a
Abul Kalam Azad was a Muslim scholar and a senior political leader of the Indian independence movement. He was one of the most prominent Muslim leaders to support Hindu-Muslim unity, opposing the partition of India on communal lines. He established an Urdu weekly newspaper in 1912 called Al-Hilal and openly attacked British police while exploring the challenges facing common people.Incorrect
Ans a
Abul Kalam Azad was a Muslim scholar and a senior political leader of the Indian independence movement. He was one of the most prominent Muslim leaders to support Hindu-Muslim unity, opposing the partition of India on communal lines. He established an Urdu weekly newspaper in 1912 called Al-Hilal and openly attacked British police while exploring the challenges facing common people. -
Question 5 of 20
5. Question
1 pointsThe song ‘Amar Sonar Bangla’ written during the Swadeshi Movement of India inspired the liberation struggle of Bangladesh and was adopted as the National Anthem of Bangladesh. Who wrote this song?
Correct
Ans d
Rabindranath Tagore wrote and composed the song “Amar Sonar Bangla” (My Golden Bengal). The song was written in 1906 when Bengal ws divided in two halves by the British Govt. on religion. The first 10 lines of the song constitute the National anthem of Bangladesh.Incorrect
Ans d
Rabindranath Tagore wrote and composed the song “Amar Sonar Bangla” (My Golden Bengal). The song was written in 1906 when Bengal ws divided in two halves by the British Govt. on religion. The first 10 lines of the song constitute the National anthem of Bangladesh. -
Question 6 of 20
6. Question
1 pointsThe First Factory Act restricting the working hours of women and children, and authorizing local governments to make necessary rules was adopted during whose time?
Correct
Ans c
The first factory Act was passed (1881) during Lord Ripon’s Viceroyship (1880-84) to improve labour conditions. Viceroy Tenure Lord Lytton 1876-80 Lord Bentinck 1828-35 Lord Canning (1st Viceroy) 1856-58, 1858-62Incorrect
Ans c
The first factory Act was passed (1881) during Lord Ripon’s Viceroyship (1880-84) to improve labour conditions. Viceroy Tenure Lord Lytton 1876-80 Lord Bentinck 1828-35 Lord Canning (1st Viceroy) 1856-58, 1858-62 -
Question 7 of 20
7. Question
1 pointsWho among the following wrote the book Babuvivah?
Correct
Ans b
Ishwar Chandra VidyasagarIncorrect
Ans b
Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar -
Question 8 of 20
8. Question
1 pointsWho wrote the book – ‘The Story of the Integration of the Indian States’?
Correct
Ans d
V.P. Menon was an Indian Civil Servant played an important role in the partition of India and the integration of Independent India during the period 1945-50.Incorrect
Ans d
V.P. Menon was an Indian Civil Servant played an important role in the partition of India and the integration of Independent India during the period 1945-50. -
Question 9 of 20
9. Question
1 pointsWhich one of the following aroused a wave of popular indignation that led to the massacre by the British at Jallianwala Bagh?
Correct
Ans c
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre took place on 13th April, 1919, when a huge crowd had assembled in Amritsar to protest peacefully against the arrest of Saifuddhin Kitchlew and Satyapal who were arrested on 10 April, 1919 for starting a Rowlatt Satyagraha against Rowlatt Act.Incorrect
Ans c
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre took place on 13th April, 1919, when a huge crowd had assembled in Amritsar to protest peacefully against the arrest of Saifuddhin Kitchlew and Satyapal who were arrested on 10 April, 1919 for starting a Rowlatt Satyagraha against Rowlatt Act. -
Question 10 of 20
10. Question
1 pointsAt which one of the following places did Mahatma Gandhi first start his Satyagraha in India?
Correct
Ans c
Champaran Satyagraha – 1917: Gandhi’s first great experiment in Satyagraha came in 1917 in Champaran, a district in Bihar. He took up the cause of the poor peasants against the excesses of the indigo planters in Champaran. He defied the government order asking him to leave the area and was willing to face trial and imprisonment. The Government was forced to inquire into the injustices committed by the indigo planters and to put an end to them. Ahmedabad Mill Strike – 1918 Kheda Satyagraha – 1918 Bardoli (Surat, Gujarat) – Satyagraha was led by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in 1928.Incorrect
Ans c
Champaran Satyagraha – 1917: Gandhi’s first great experiment in Satyagraha came in 1917 in Champaran, a district in Bihar. He took up the cause of the poor peasants against the excesses of the indigo planters in Champaran. He defied the government order asking him to leave the area and was willing to face trial and imprisonment. The Government was forced to inquire into the injustices committed by the indigo planters and to put an end to them. Ahmedabad Mill Strike – 1918 Kheda Satyagraha – 1918 Bardoli (Surat, Gujarat) – Satyagraha was led by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in 1928. -
Question 11 of 20
11. Question
1 pointsWho among the following started the newspaper Shome Prakash?
Correct
Ans b
A Bangali newspaper ‘Somprakash’ was started in 1898 by Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar.Incorrect
Ans b
A Bangali newspaper ‘Somprakash’ was started in 1898 by Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar. -
Question 12 of 20
12. Question
1 pointsThe ruler of which one of the following States was removed from power by the British on the pretext of mis-governance?
Correct
Ans a
During the administration of Nawab ‘Wazid Ali’, Awadh was annexed under the pretext of misrule.Incorrect
Ans a
During the administration of Nawab ‘Wazid Ali’, Awadh was annexed under the pretext of misrule. -
Question 13 of 20
13. Question
1 pointsWho among the following Europeans were the last to come to pre-independence India as traders?
Correct
Ans c
Entry of European powers in India: Portuguese – 1548 English – 1600 Dutch – 1902 Danish – 1616 French – 1664Incorrect
Ans c
Entry of European powers in India: Portuguese – 1548 English – 1600 Dutch – 1902 Danish – 1616 French – 1664 -
Question 14 of 20
14. Question
1 pointsConsider the following statements:
1. Robert Clive was the first Governor-General of Bengal.
2. William Bentinck was the first Governor-General of India.
Which of the statements given below above is/are correct?Correct
Ans b
Warren Hastings was the first Governor-General of Bengal as per the Regulating Act of 1773.Incorrect
Ans b
Warren Hastings was the first Governor-General of Bengal as per the Regulating Act of 1773. -
Question 15 of 20
15. Question
1 pointsWhich one of the following was the first fort constructed by the British in India?
Correct
Ans b
Fort. St. George – 1644 (Madras) – British Fort William – 1700 (Calcutta) – British Fort St. David – Fort sold by Marathas to British in 1690. Fort St. Angelo –Built by Portuguese in 1505 at Kannur (Kerala).Incorrect
Ans b
Fort. St. George – 1644 (Madras) – British Fort William – 1700 (Calcutta) – British Fort St. David – Fort sold by Marathas to British in 1690. Fort St. Angelo –Built by Portuguese in 1505 at Kannur (Kerala). -
Question 16 of 20
16. Question
1 pointsWhich one of the following places was associated with Acharya Vinoba Bhave’s Bhoodan Movement at the beginning of the movement?
Correct
Ans c
Eminent Gandhian constructive worker Acharya Vinoba Bhave, drew upon Gandhian techniques and ideas such as constructive work and trusteeship, to launch the Bhoodan Movement in early fifties (1950’s). Vinoba Bhave received the first donation of land on 18 April 1951 in the village of Pachampalli in the Telangana district of Andhra Pradesh.Incorrect
Ans c
Eminent Gandhian constructive worker Acharya Vinoba Bhave, drew upon Gandhian techniques and ideas such as constructive work and trusteeship, to launch the Bhoodan Movement in early fifties (1950’s). Vinoba Bhave received the first donation of land on 18 April 1951 in the village of Pachampalli in the Telangana district of Andhra Pradesh. -
Question 17 of 20
17. Question
1 pointsAssertion (A): According to the Wavell Plan, the number of Hindu and Muslim members in the Executive Council were to be equal.
Reason (R): Wavell thought that this arrangement would have avoided the partition of India.
Correct
Ans c
Wavell Plan proposed a council with equal numbers of Hindus and Muslims, and one representative each of Sikhs and the Depressed classes, besides the Commander in chief and the main purpose was to delay the process of partition but not to avoid partition.Incorrect
Ans c
Wavell Plan proposed a council with equal numbers of Hindus and Muslims, and one representative each of Sikhs and the Depressed classes, besides the Commander in chief and the main purpose was to delay the process of partition but not to avoid partition. -
Question 18 of 20
18. Question
1 pointsWho was the Governor-General of India during the Sepoy Mutiny?
Correct
Ans a
Lord Canning was the Governor-General of India during the Sepoy Mutiny. He was the last and first Governor General and Viceroy of British India respectively.Incorrect
Ans a
Lord Canning was the Governor-General of India during the Sepoy Mutiny. He was the last and first Governor General and Viceroy of British India respectively. -
Question 19 of 20
19. Question
1 pointsConsider the following statements about Madam Bhikaji Cama:
1. Madam Cama unfurled the National Flag at the International Socialist Conference in Paris in the year 1907.
2. Madam Cama served as private secretary to Dadabhai Naoroji.
3. Madam Cama was born to Parsi parents.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Ans b
Madam Cama held aloft the flag of Indian Freedom by taking part in International Conference at Stuttegaurd in Germany on 18 August 1907.Incorrect
Ans b
Madam Cama held aloft the flag of Indian Freedom by taking part in International Conference at Stuttegaurd in Germany on 18 August 1907. -
Question 20 of 20
20. Question
1 pointsConsider the following statements:
- The Charter Act 1853 abolished East India Company”s monopoly of Indian trade.
- Under the Government of India Act, 1858, the British Parliament abolished the East India Company altogether and undertook the responsibility of ruling India directly.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Ans b
The Charter Act of 1813 abolished East India Company’s monopoly of Indian trade except for trade in tea and trade with China. Charter Act 1833 abolished company’s monopoly of trade in tea and trade with ChinaIncorrect
Ans b
The Charter Act of 1813 abolished East India Company’s monopoly of Indian trade except for trade in tea and trade with China. Charter Act 1833 abolished company’s monopoly of trade in tea and trade with China
