Mahajanapadas Notes with PDF
These notes are your ultimate revision weapon to revise Mahajanapadas. We’ve distilled years of previous exam questions (PYQs) into one powerful, concise resource. Everything you need to know, nothing you don’t.
- PYQs, Decoded: All key concepts from past exams, organized and simplified.
- Revise in Record Time: Short, precise, and designed for last-minute review.
- Focus on What Matters: Master high-probability topics and boost your confidence.
- Free PDF to download.
You'll Read
Ancient Indian Kingdoms and Dynasties
1. The Mahajanapadas (The 16 Great Kingdoms)
- General Facts:
- Existed in the 6th century BCE.
- There were 16 major kingdoms (Mahajanapadas).
- 8 were located in the region of present-day Uttar Pradesh: Kuru, Panchala, Kosala, Kashi, Vatsa, Malla, Chedi, and Shurasena.
- Sources:
- Listed in the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya and the Jain text Bhagwati Sutra.
- The grammarian Panini also listed 22 Janapadas in his work Ashtadhyayi.
- Specific Kingdoms and Capitals:
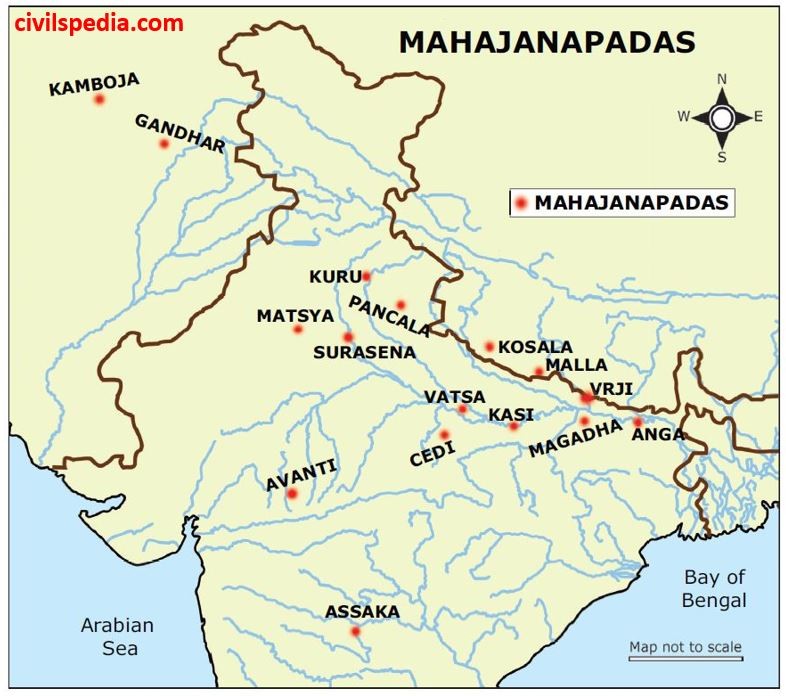
-
- Anga: Capital was Champa (modern Munger & Bhagalpur, Bihar). Later annexed by Magadha.
- Magadha: Initial capital was Rajgriha (Girivraja). Later moved to Pataliputra.
- Kosala: Capital was Shravasti (which had a crescentic town configuration). Also associated with Saket.
- Vatsa: Capital was Kaushambi.
- Avanti: Capital was Ujjain (ancient name: Avantika).
- Chedi: Capital was Suktimati (Sotthivati). Located in the Bundelkhand region.
- Surasena: Capital was Mathura.
- Matsya: Located in present-day Rajasthan (around Jaipur). Capital was Viratnagar.
- Panchala: Divided into two parts.
- North Panchala: Capital was Ahichhatra.
- South Panchala: Capital was Kampilya.
- Kuru: Capitals were Indraprastha and Hastinapur.
- Assaka (Ashmaka): Capital was Potana/Potali (modern Paithan). Located between the Godavari and Narmada rivers.
- Republics (Gana-Sanghas):
- Lichchhavis established a republic at Vaishali (perhaps the first republic in the world).
- Chetak was the leader of the Lichchhavi clan (part of the Vajji confederacy).
- Other ancient republics included the Shakyas (of Kapilavastu) and the Yaudheyas.
2. The Magadha Empire
- Dynasties and Chronological Order:
- Haryanka Dynasty (544 – 412 BCE)
- Shishunaga Dynasty (413 BCE to 343 BCE)
- Nanda Dynasty (344 – 321 BCE)
- Maurya Dynasty (321 – 184 BCE)
- Shunga Dynasty (184 – 75 BCE)
- Key Rulers and Events:
- Haryanka Dynasty:
- Bimbisara: Key founder who started Magadha’s rise. Patronized the physician Jivaka.
- Married Chelana, daughter of Lichchhavi leader Chetak.
- Ajatashatru: Son of Bimbisara, killed his father to take the throne.
- Udayin (Udayan/Udayabhadra): Son of Ajatashatru, who killed him. Founded the city of Pataliputra and moved the capital from Rajgriha to there.
- Shishunaga Dynasty:
- Sishunaga: Extended Magadha’s power by defeating Avanti and conquering the Malwa region.
- Nanda Dynasty:
- Founder: Mahapadma Nanda (also known as Ugrasena).
- Titles: Called Sarakshatrantaka (destroyer of all Kshatriyas) and Aparo Parashurama (the second Parashurama) in the Puranas.
- Conquered Kalinga and dug a canal there, as recorded in the Hathigumpha Inscription, with King Kharavela later extending it to his capital, Kalinganagari.
- Last Ruler: Dhanananda.
- Downfall: Ended due to public unhappiness over high taxes. Chandragupta Maurya and Chanakya overthrew Dhanananda.
- Haryanka Dynasty:
3. Other Notable Rulers and Historical Figures
- Pradyota Dynasty (Avanti):
- Pradyot (Chand-pradyota): Ruler of Avanti. A contemporary of Gautama Buddha and Bimbisara. Was treated by physician Jivaka.
- Kosala:
- Prasenjit was a ruler of Kosala.
- Vatsa:
- Udayana was a ruler of the Vatsa Mahajanapada.
- Chedi Dynasty (Kalinga):
- Kharavela: A major ruler. His Hathigumpha inscription records:
- The first evidence of canal construction in Kalinga.
- Donations of villages to Jain monks.
- Victories over southern states like the Cholas, Cheras, and Pandyas.
- Kharavela: A major ruler. His Hathigumpha inscription records:
- Later Period:
- Mahendra was the ruler of Kosala during Samudragupta’s time (as per the Prayag Prashasti).
- Scholars:
- Panini: A famous Sanskrit grammarian born in Pushkalavati, Gandhara. His most important work is the Ashtadhyayi, in which he mentioned the Janapadas of Magadha, Ashmak, and Kamboj.
- Archaeologists:
- Alexander Cunningham: A British archaeologist who identified the ancient city of Shravasti (near modern Gonda, UP) in 1861.
4. Important Cities and Geography
- Pataliputra:
- Founded by Udayin of the Haryanka dynasty.
- Established as a fort at the confluence of the Son and Ganga rivers.
- Became the capital of major empires like the Mauryan, Nanda, and Shishunaga dynasties.
- Chandragupta Maurya was the first emperor to make it the capital of a large empire.
- Ujjain:
- Ancient name was Avantika.
- Associated with the legend of Udayan and Vasavadatta.
- Other Ancient Cities:
- Viratnagar (Bairat) and Madhyamika (Nagari) are ancient cities mentioned in both the Mahabharata and Patanjali’s Mahabhashya.
- Historical Geography of Uttar Pradesh:
- Kalpi: An ancient town on the bank of the Yamuna River (Jalaun district). Known as Kalpriya in ancient times, founded by King Vasudeva in the 4th century BC.
- Kaushambi: The capital of the Vatsa Mahajanapada.
- Ahichhatra: The capital of the Panchala Mahajanapada.
- Medieval Name Changes:
- Koil is the old name for Aligarh.
- Mahotsav Nagar is the old name for Mahoba (meaning ‘city of great festivals’).
- Mahodaya Shree is the old name for Kannauj (once the capital of Harsha’s empire).
- Jejakabhukti is the old name for the Bundelkhand region.
5. Religion, Philosophy, and Society
- 6th Century BCE Context:
- A period of significant religious upheaval and intellectual questioning across the world (e.g., Confucius in China, Zarathustra in Iran, Pythagoras in Greece).
- In India, this was due to the complexity of Vedic religion, which had become overly focused on rituals and sacrifices, increasing the power and cost of priestly classes.
- This environment led to the emergence of new heterodox faiths like Buddhism and Jainism.
- Other Dynasties (Post-Mauryan):
- The Karnata Dynasty’s last king was Harisimha Dev (Mithila), who was a patron of art and literature and created the Panji system (a method for recording and preserving the genealogy of certain castes).
6. Ancient Indian Coins
- Earliest Indian Coins:
- The oldest extant coins of India were made of silver.
- They are known as Punch-marked or Aahat coins.
Know More about the Mahajanapadas :
